3D Cut Software
In this document, we will walk you through the basic interface of the program and how to prepare a 3D cut file for the ShopBot machine. This example shows how to mill a model that fits on one block of material. If your model is more complex and requires milling more than one piece, please consult the Fab Lab staff.
- After creating your 3D file, export it into .stl, or .obj. Open the file in the software by opening the “model” drop down menu and selecting “Import Component/3D Model.” Left click to rotate the model; right click to zoom; left and right click to pan.
After a file is loaded, you will see these icons and options in the interface:
- Initial Orientation: To flip a model on the surface of x and y.
- Interactive Rotation: To freely rotate your 3D model.
- Model Size: put the exact number of the model’s size. The numbers need to fit within the material you will use. If you will mill a model from one material (no sliced layers) you have to scale the z to fit with the material height. If the ratio doesn’t matter, uncheck the “Lock XYZ ratio” to change the number freely.
- Units: Stay in Inches because the machine works in inches.
- Zero Plan Position in Model: To position the depth of your 3D model inside your stock material.
2. After choosing your settings in step 1, click the OK button to move onto the “3D Model Tools” menu. In the modeling workspace you can:
- Import a component or 3D model.
- Look at and change the properties of your component.
- Create a vector boundary for machining your component.
- Apply a smoothing filter to your component.
- Scale the Z height of your model.
- Slice your model into individual components.
- Add a plane component to your model
3. If you are cutting your shape out of the stock material you will need to add tabs to hold the model to the leftover material. To do this go to the “cliptart” tab at the bottom of the modeling menu on the left and then click on the “3D Tabs” folder. Find your desired tab shape and then drag and drop as many tabs as you need onto your model. From here you can adjust the dimensions of your tab by clicking the component properties icon back in the modeling menu. 4. After you are satisfied with the orientation, scale, and tabs of your model select the “Toolpaths” menu on the right side of the screen. You can “pin” it so it won’t close automatically when you click somewhere else. You should see these icons on the right side of the screen in your interface.
4. After you are satisfied with the orientation, scale, and tabs of your model select the “Toolpaths” menu on the right side of the screen. You can “pin” it so it won’t close automatically when you click somewhere else. You should see these icons on the right side of the screen in your interface.
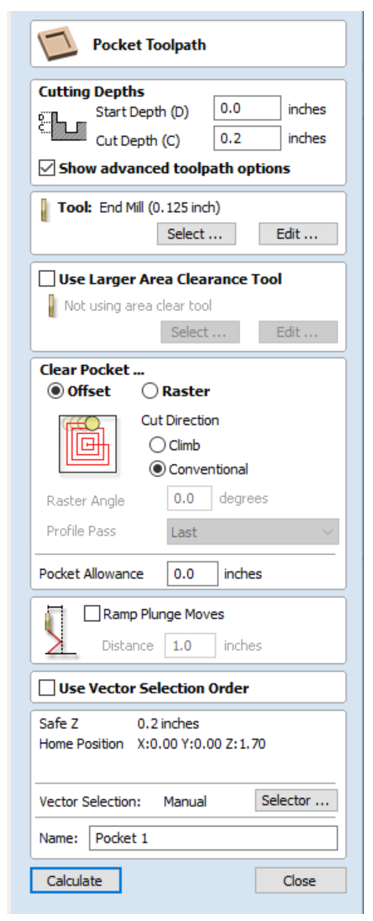
4. Before we begin creating our toolpath we need to check our material setup. To do this click the button that says “Set…” under the Material Setup heading.
After you click the “Set..” button, you will see these icons and options in the interface:
- Thickness: Adjust the thickness of your stock material.
- XY Datum: Set the X,Y Zero position in relation to your stock material.
- Z-Zero: Sets the Z Zero position to either the top of your stock material or to the machine bed.
- Model Position in Material: This is where your model is in relation to your stock material. The light brown portion is the actual model and the dark brown is the amount of stock material above and below your model.
- Rapid Z gaps above Material: This sets the amount of distance between the tool and your material. You should not need to adjust this.
- Home / Start Position: You can adjust where you want the machine to start from, you will almost always keep this at X=0 , Y=0.
5. Once you have your material set up correctly select “3D Roughing Toolpath” to get started with a toolpath that will remove the bulk of your material with an end mill. After you click the roughing toolpath button, you will see these icons and options in the interface: